Allied Kommandatura

The Allied Kommandatura, or often just Kommandatura, also known as the Alliierte Kommandantur in German, was the governing body for the city of Berlin following Germany's defeat in World War II. The victorious allied powers established control of post-war Germany and other territories via shared Military Government councils, including for Berlin. The Kommandatura was often known as the little brother[1] to the Allied Control Council, which had the same function for the whole of Germany, and was subordinate to it.[2] It originally comprised representatives from the United States, the United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union but later included France. The Kommandatura had its home in the Berlin district of Dahlem.[3]
Creation
President Roosevelt declared at the Casablanca Conference in early 1943 that the goal of the war was the unconditional surrender of Germany. To that end, and during the following many months, the leading Allied powers planned and gave form to the task of dividing Germany, and how to govern her after the war. The London Protocol of September 1944, established the division of Germany into zones of occupation, and the city of Berlin into sectors. Additionally, Berlin was to be governed by an Allied Komendatura (sic).
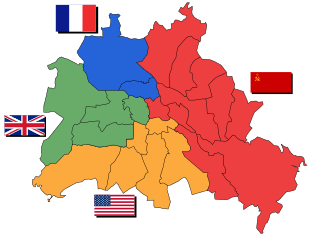
The Soviets fought for and captured Berlin by the beginning of May 1945, and set up camp not only their own sector, but took control over the whole of Greater Berlin. The U.S. and British entered Berlin later, on July 1, and July 24, respectively. By that time the Soviets had plundered and pillaged the western sectors of Berlin. They had removed vital industrial infrastructure on a wholesale scale, and had taken most of what was left in the city in terms of agriculture and livestock.[4]
The U.S. commandant, Major General Floyd L. Parks, tasked his divisional G5 and later deputy, Colonel Frank L. Howley,[5] to prepare a general plan for the basis of an Allied Kommandatura, based on a Russian proposal.[6] Howley had arrived in Berlin July 1, 1945,[7] as leader of the joint U.S.–British Military Government detachment, although the U.S. didn't take over their sector officially until July 12, when the Russians finally moved out.[8] By this time the French had also obtained their own sector in the north of Berlin, carved out of the British sector, but were not invited to participate in the initial meetings.[9]
In any case, Howley's plan was in preparation for the first high-level post-war meeting between the Allies regarding Berlin, and outlined conditions for quadripartite governance. General Lucius D. Clay, Eisenhower's deputy, Robert Murphy, Eisenhower's political adviser, and others flew in to Berlin for the meeting. Berlin's fate was sealed, however, prior to the July 7 meeting. Clay and others let Parks know, in no uncertain terms, that Berlin was to be governed unanimously in all instances. Howley's plan was carefully worked out and allowed governance on a divided basis when unanimity could not be obtained, but Clay was following orders from Washington. General Clay and the British, including Gen. Sir Ronald Weeks and Sir William Strang, were caught flat-footed at the meeting, and subsequently deferred to the Soviets on so many issues. Their chief representatives were Marshals Zhukov and Sokolovsky, both of whom had great experience in moving a situation to their advantage. Howley indicated that the signed "Komandatura agreement put the Soviets in the saddle."[10]
The next meeting on July 11, 1945, represented the first actual meeting of the Allied Kommandatura, where the four-power Council of Commandants began governing the city.[11] One major, initial task remained: where to meet. This was left to the Kommandatura deputies to resolve. The Soviets offered one possible location for Kommandatura headquarters, but it was far removed in a distant Berlin suburb. The British offered several damaged buildings and a hotel in their sector. Howley initially offered a building on Lake Wannsee, but others objected that they would never get any work done in such a beautiful setting. Finally he suggested another site not far distant from the American military headquarters, which was accepted by all on the condition that it was made serviceable.[12]
Operation
In theory the Kommandatura would decide issues requiring attention and governance, formulate a response, and issue formal orders to the Lord Mayor and the Berlin Magistrat.[13] At the July 11, 1945, meeting, the commandants signed the first of their nearly 1300 such quadripartite orders. That particular order truly put the Soviets in the saddle as it reinforced all preexisting Russian regulations and ordinances put in place throughout the city before the western allies arrived:

The Inter-Allied Kommandatura has today assumed control over the city of Berlin. Until specific notice, all existing regulations and ordinances issued by the Commandant of the Soviet Army Garrison and Military Commandant of the City of Berlin, and by the German administration under Allied control, regulating the order and the conduct of the population of Berlin, and also the liability of the population for the violation of such regulations and ordinances, or for unlawful acts against Allied occupation troops, shall remain in force.[14]
Thereafter, anytime the Western Allies protested a specific Russian action, they responded that they were simply abiding some statute or regulation that was already in place before the Americans, British, or French arrived. Anytime the Russians were asked to produce the regulation in question, they refused. Of such was the foundation of the newly formed four-power council.[15]
At first all Kommandatura meetings were strictly at the highest level, meaning the sector commandants. Out of necessity other meetings grew up, including meetings of deputies and committees, etc. The deputies were able to decide a vast majority of issues and questions at their own meetings, and passed on to their commanders only the most vital of items or when a decision could not be reached.[16] Also, on occasion things were kicked up to the Allied Control Council when a consensus could not be reached on something of crucial importance by the Kommandatura,[17] and perhaps kicked back down when the zonal commanders didn't want to be bothered by it.[18]
In the beginning meetings were informal, and rules of procedure grew as they went along. The chairmanship changed every two weeks, but later it was monthly. The Russians won a coin toss at the suggestion of General Parks, and they filled the first chair. The Americans and British followed in rotation, along with the French after about three months.[19] Even the position of the flags on the poles out in front of the Kommandatura headquarters rotated along with the chairmanship. Inside the Kommandatura the four commandants met in the main conference room, and sat at a large rectangular table with the chairman at the head. If the Union Jack was flying out front, the British commandant was at the head of the table, with the French commander to his right, and across the table the Russian representative, and next to him the American. Adjacent to each commandant was his deputy and political adviser. Groups of experts on divers topics rounded out much of the remainder of the personnel in the room, along with translators and clerical staff.[20]

The myriad committees met in many of the other rooms in the Kommandatura building, and handled routine work, issued orders to the city government, and worked through items not yet agreed upon. All such work was sent to the deputies at their respective meetings twice a month in the main conference room. Many such items were scrutinized for presentation at the commandants' meetings. There was so much work to get through, they had to develop a streamlined procedure to reduce everything to the bare essentials, else they "would have been swamped by bitter international wranglings," Howley states.[21]
Language translation itself was cumbersome, but obviously necessary. Each commandant had translators selected for him by the respective Chiefs of Staff to handle the various parts of the discussion. These stood behind each respective commandant. When the American spoke, it was translated into French by the Frenchman's translator, and into Russian from the French by the Soviet commandant's translator. The Russian translator didn't understand English, but spoke excellent Russian and French. Each commandant would speak in staccato fashion to make easier work for the translators. Notes flowed constantly from the myriad advisers in the room to the commandants. Howley intimated he likely would have never lasted without those notes. They clarified, and probed, and shattered the arguments of others.[22]
Soviet walkout
As time passed, the quadripartite meetings of the Kommandatura got more and more heated and cantankerous. The western allied representatives were more or less unified in their view of how Berlin was to be governed, which often starkly contrasted with the Soviet point of view, not surprisingly so. Issues would be debated for weeks, and even months. One such issue was Kotikov's Fourteen Points regarding the legal and material position of the workers of Berlin. For eight months the Kommandatura debated this topic making no real headway. Without Kommandatura approval, the Soviet Military Administration issued Order No. 20 in their own sector, making all fourteen points law. This did not sit well with the others, nor did it abide the spirit of quadripartite and unanimous city governance.[23]

During the Kommandatura meeting of June 16, 1948, the current chairman, French commandant General Ganeval, proposed that the Soviets rescind Order No. 20, so that the fourteen points could be individually reviewed and discussed. Up until that time the Soviets insisted on an all or nothing approach. They refused to rescind the order unless all other delegations agreed to the fourteen points unanimously and issued a quadripartite agreement to the effect of the same for the whole of Berlin. Discussions on this and other issues had dragged on for over thirteen hours at that point, and it was nearing midnight. That's when the American commandant, Colonel Howley, asked to be excused, as he had a heavy schedule planned for the following day. Chairman Ganeval gave permission, and Howley left his deputy, Colonel Babcock, in charge, just as he had done in times past when the situation required it.[24]
After Howley's departure, reports state that Colonel Yelizarov, Kotikov's deputy filling in for the supposedly ill Soviet commandant, held an excited, whispered exchange with their political commissar, L. M. Maximov. Yelizarov then stood and took offense at Howley's departure, and labeled it a "hooligan action." (Howley and Yelizarov already had a history. Howely described him as a "big, powerful, bruiser," who hunted wild boar with a machine gun in the woods outside Berlin. "He and I always kept one hand on the trigger.")[25] At that point Ganeval proposed to close the meeting, but Yelizarov would have none of it. For eight minutes he berated an absent Howley, and offered that the Soviet delegation could no longer remain unless Howley return and apologize to all. Yelizarov headed for the door with Maximov closely in tow, whilst Ganeval reminded them that Howley had been properly excused. The French chairman indicated that it was indeed Yelizarov who was out of order and not Howley. The Russians departed in a maelstrom of confusion, but the record shows Ganeval closed the meeting due to the departure of the Soviet delegation and not Howley's excused absence.[26]
There were likely many things that contributed to the breakup. There was a rumored currency reform for the western zones of Germany, which actually did happen later.[27] But unbeknownst to the western allies at the time, the Soviets had planned to blockade Berlin in mere days. In the end, the breakup of the Allied Kommandatura had been a planned work in progress for quite some time, according to Howley,[28] as it suited the purposes of the Soviets, period. It followed the pattern of the breakup of the Allied Control Council, when three months earlier Marshal Sokolovsky staged the walkout then.[29]
For the balance of June, the Soviets did participate in limited quadripartite sub-committee meetings, and their clerical staff remained through July. But as of August 1, 1948, they lowered the red flag, removed their files, and the Soviets were gone for good. After that the three western sectors operated independently and unilaterally for a time. They resumed official Kommandatura meetings on November 8, 1948, but then only ever on a tripartite basis.[30]
Accomplishments
The differences in goals and methods of the East and the West, which came face to face in Kommandatura counsels so frequently, and which usually always clashed, have their roots elsewhere. But despite the stark philosophical divide that existed at the Kommandatura, much good was accomplished despite the interminable wranglings. The official Four Year Report[31] states:
We have succeeded in giving Berlin a complete school reform, which is the basis for the end of class distinction in the city. We have created a city constitution and held city-wide elections under four-power supervision. Nazis were removed from all levels of public influence. The number of agreements at the Allied Kommandatura exceeds 1,200 and even includes agreed loans to Catholic, Protestant, and Jewish churches. We have succeeded in reviving the social and political life of the city. We have guided Berlin Germans to a concept of democracy similar to our own.[32]
Howley stated further, and not surprisingly so, that there was no success in smoothing over the divide between politics and philosophy. They couldn't even agree on the control of potato bugs, "because the boys from Moscow insisted on making potato bugs a political issue—which was the first time I ever knew that a slug comprehended the dialectics of materialism according to Marx," he said.[33]
The Soviets instituted a general blockade of Berlin on June 24, 1948. The western Allies responded with an airlift, the first time such a thing was ever devised, especially to provide for a city as large as the western part of Berlin. The state of relations continued to devolve from that point on.
The Kommandatura building

Until they had devised a new, permanent headquarters, the Kommandatura met in the Soviet sector for several weeks, in rooms of the Soviet Central Kommandantur.[34] Shortly thereafter the new headquarters was ready to be occupied, and on July 25, 1945, the Kommandatura met at Kaiserswerther Str. 16-18 in Berlin-Dahlem for the first time. The building was in constant use as Kommandatura headquarters until March 15, 1991, when the Two Plus Four Agreement went into effect.[35]
The building was formerly the administration building for Public Fire Insurance Carriers in Germany (Verbandes der öffentlichen Feuerversicherungsanstalten). It was designed by Heinrich Straumer, designer and builder of the Funkturm Berlin, and was built between 1926-1927. Since 1994 it has been used as the office of the President of the Free University of Berlin (Präsidialamt).[36]
See also
- Allied-occupied Austria
- European Advisory Commission
- Four Power Agreement on Berlin
- History of Berlin
- List of Commandants of Berlin Sectors
- Military occupation
References
- ↑ Article, Allied Control Council (ACA) and The Allied Kommandatura. Retrieved: 25MAY13
- ↑ Berlin Command, Brig. General Frank Howley, 1950, page 6
- ↑ Article, Allied Control Council (ACA) and The Allied Kommandatura. Retrieved: 25MAY13
- ↑ Berlin Command, Brig. General Frank Howley, 1950, pages 44-45
- ↑ Berlin Command, Brig. General Frank Howley, 1950, page 45
- ↑ Berlin Command, Brig. General Frank Howley, 1950, page 52
- ↑ Berlin Command, Brig. General Frank Howley, 1950, pages 42-44
- ↑ Berlin Command, Brig. General Frank Howley, 1950, page 51
- ↑ Berlin Command, Brig. General Frank Howley, 1950, page 52
- ↑ Berlin Command, Brig. General Frank Howley, 1950, pages 52-59
- ↑ Berlin Command, Brig. General Frank Howley, 1950, page 61
- ↑ Berlin Command, Brig. General Frank Howley, 1950, pages 62-63
- ↑ A Four Year Report, Office of Military Government U.S. Sector, Berlin, 01JUL45-01SEP49, page 24. Retrieved: 25MAY13
- ↑ A Four Year Report, Office of Military Government U.S. Sector, Berlin, 01JUL45-01SEP49, page 25. Retrieved: 25MAY13
- ↑ Berlin Command, Brig. General Frank Howley, 1950, pages 61-62
- ↑ Berlin Command, Brig. General Frank Howley, 1950, page 62
- ↑ Berlin Command, Brig. General Frank Howley, 1950, pages 56, 84, 86, 102, 112, 121, etc
- ↑ Berlin Command, Brig. General Frank Howley, 1950, pages 110, 137
- ↑ Berlin Command, Brig. General Frank Howley, 1950, pages 63-64
- ↑ Berlin Command, Brig. General Frank Howley, 1950, page 157
- ↑ Berlin Command, Brig. General Frank Howley, 1950, pages 157-158
- ↑ Berlin Command, Brig. General Frank Howley, 1950, pages 158-159
- ↑ Breakup of the Allied Kommandatura. Retrieved: 15APR13
- ↑ Berlin Command, Brig. General Frank Howley, 1950, pages 180-181
- ↑ Tales from Spandau: Nazi Criminals and the Cold War, Norman J. W. Goda, 2006, pages 41-42
- ↑ Berlin Command, Brig. General Frank Howley, 1950, pages 181-182
- ↑ Berlin Command, Brig. General Frank Howley, 1950, page 184
- ↑ Berlin Command, Brig. General Frank Howley, 1950, pages 176
- ↑ Berlin Command, Brig. General Frank Howley, 1950, pages 177-178
- ↑ Berlin Command, Brig. General Frank Howley, 1950, page 257
- ↑ A Four Year Report, Office of Military Government U.S. Sector, Berlin, 01JUL45-01SEP49, page 7. Retrieved: 25MAY13
- ↑ Berlin Command, Brig. General Frank Howley, 1950, page 7
- ↑ Berlin Command, Brig. General Frank Howley, 1950, page 7
- ↑ Alliierte Kommandantur. Retrieved: 15APR13
- ↑ Alliierte Kommandantur. Retrieved: 15APR13
- ↑ Alliierte Kommandantur. Retrieved: 15APR13